Connected Home vs Smart Home
People believe “smart homes” and “connected homes” are the same. You might even see terms like “true smart home”, where companies try to bring their point across of having a home, which is more than an assembly of connected devices. Let’s look into those terms and define, what a “smart home” really is.
Let’s start with the official definition outlined by Wikipedia. Smart House on Wikipedia refers to Home Automation. Within Home Automation you will find the following definition.
“Home automation or smart home (also known as domotics or domotica) is the residential extension of building automation. It involves the control and automation of lighting, heating (such as smart thermostats), ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), and security, as well as home appliances such as washer/dryers, ovens or refrigerators/freezers. They use Wi-Fi for remote monitoring and are a part of the Internet of things. Modern systems generally consist of switches and sensors connected to a central hub sometimes called a “gateway” from which the system is controlled with a user interface that is interacted either with a wall-mounted terminal, mobile phone software, tablet computer or a web interface, often but not always via internet cloud services.“
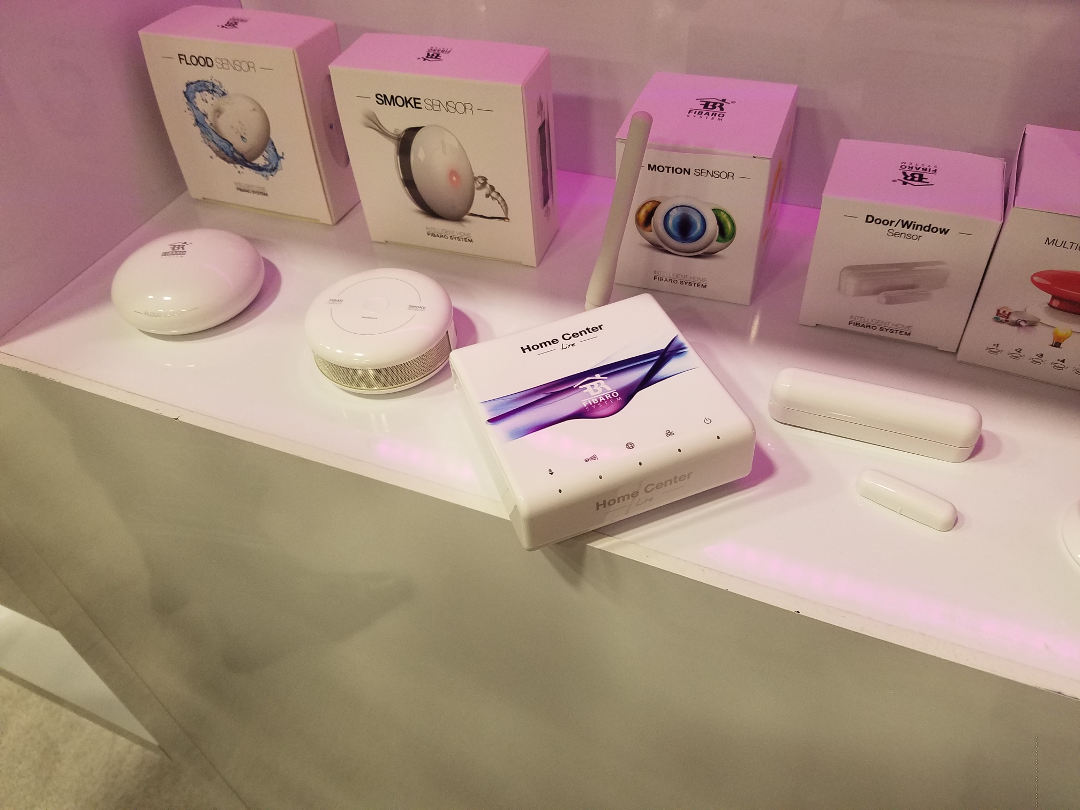
The key word here is “automation”. Putting so called “smart devices” into a home doesn’t make the home smart. The industry is using the term “smart” for devices, which can be controlled by a smart phone, tablet or nowadays voice control devices like Amazon Echo or Google Home. Another example would be the trend of smart doorbells. Just because a doorbell will notify you on your cell phone, emails or texts you or allows you to speak to your visitor from your cell phone with two-way audio, doesn’t mean you have a smart home.
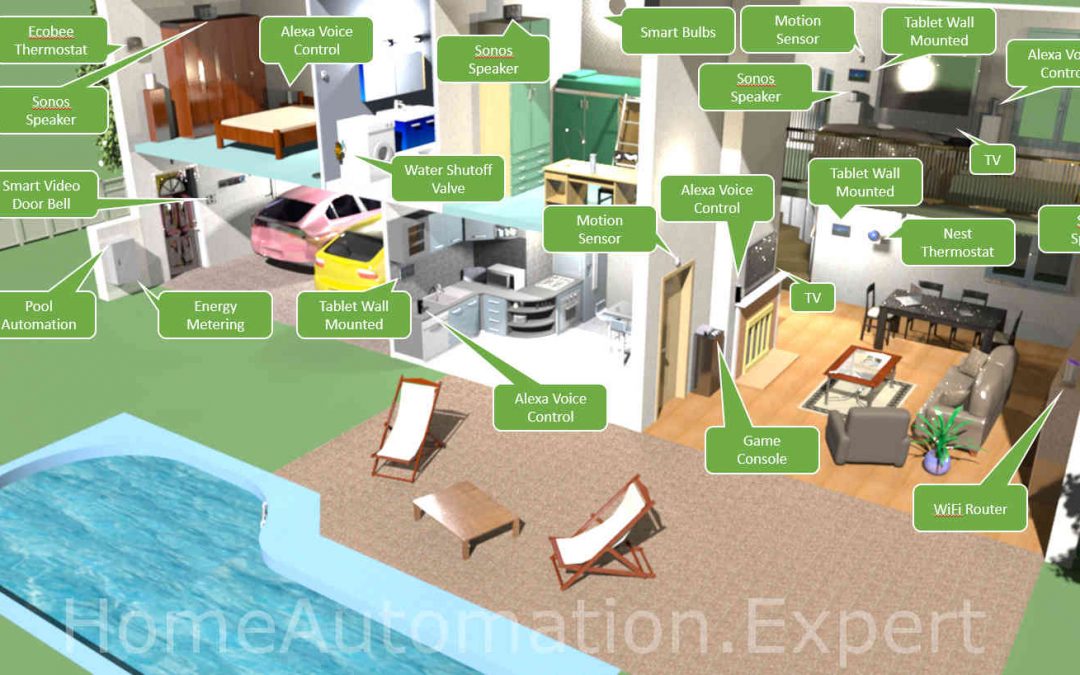
I created the following picture to demonstrate one example home with smart devices and then I will go into the details with real life use cases/examples of what would make this home a “smart home”.
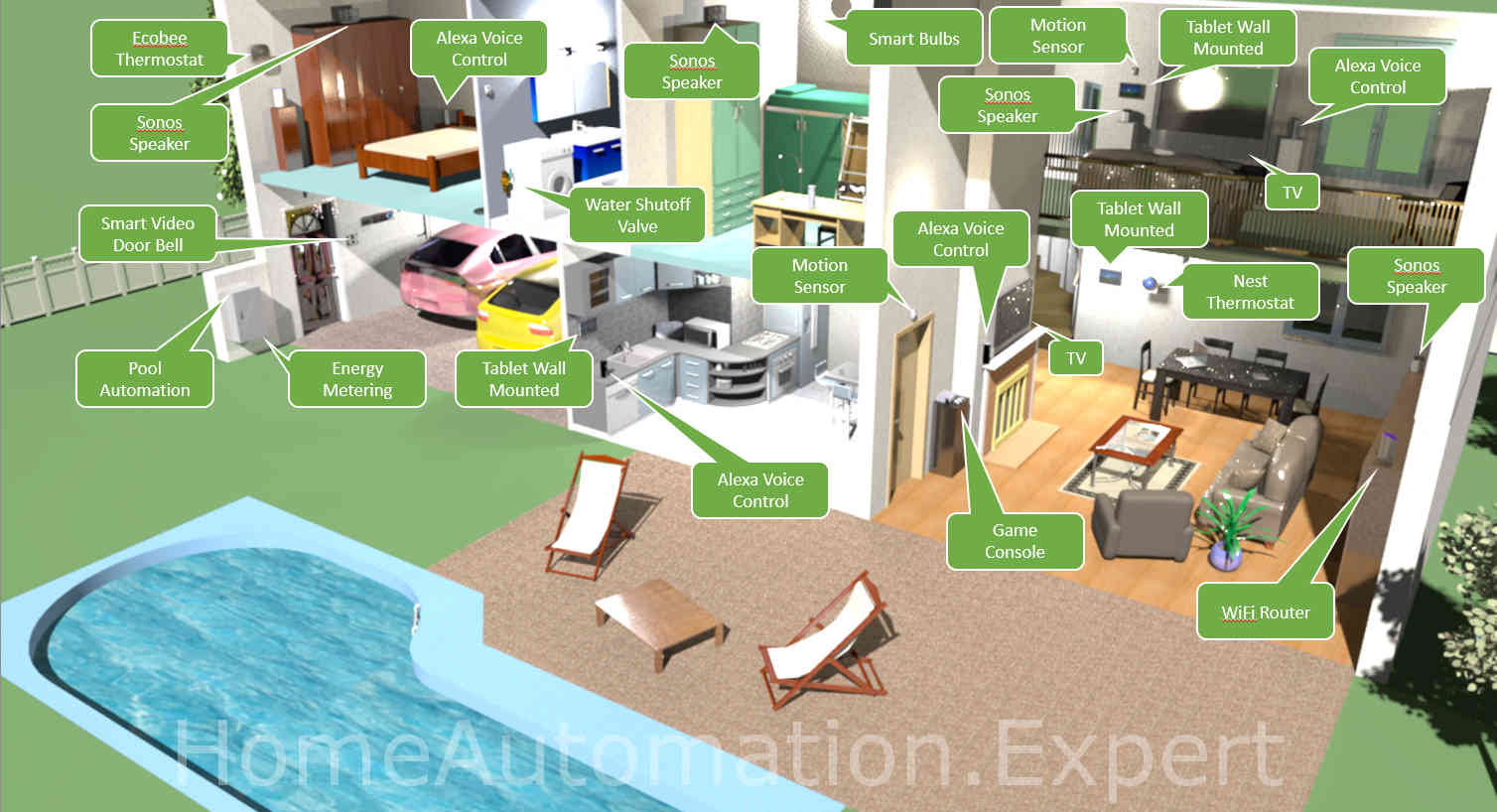
You can see a lot of devices within this “smart home” ranging from thermostats, speakers, media and entertainment, etc. Most or all of those devices can be controlled from a smart phone, tablet or Alex Echo / Google Home with individual apps or skills (as Amazon calls them). They don’t have to be necessarily have to controlled by a single home automation hub/controller/gateway.
With that said, let’s provide some examples, where the true benefit of having a home automation hub/controller/gateway will showcase, what a “smart home” should look like, otherwise this home would simply be a “connected home”.
Geo Fencing
The most common use case is GEO fencing. GEO fencing is the term for location aware reaction of your home automation system.
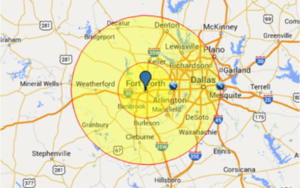 In this example you create either one or two virtual fences around your home. The first fence is very close proximity e.g. 100 to 200 feet to capture if you leave your home. The second fence could be a couple of miles.
In this example you create either one or two virtual fences around your home. The first fence is very close proximity e.g. 100 to 200 feet to capture if you leave your home. The second fence could be a couple of miles.
Most people go with one fence only but others go with a second one to e.g. set the temperature of the home to a more comfortable setting so by the time they get home, the house is nice and cool or warm and cozy and if it is night, turn on the lights in certain areas of your home and open the garage door, when you approach the inner perimeter.
Yes, you could use your cell phone and open your Nest or Ecobee app, while you are driving, and set the temperature to the desired level. You could press the button in your car to open the garage door, when you are in front of it. The Geo fencing feature does all that for you based on logic you defined and if any delay occurs like traffic jam on the highway, you wouldn’t have to worry about opening your app and changing states of your smart devices.
Disaster Prevention
Less known, but very efficient and effective example is the combination of water shut-off valves and water leak sensors. In the old days you could buy a system, which connected to a telephone line and if the water leak sensor detected a leak, it called out and notified specific people. Those systems were expensive in up front cost and in some cases they charged monthly fees for that service.
In addition to that, the sensors were limited in terms of how many of those sensors could be installed and how long those wires could have been. Those costs and limitations prohibited a wide deployment of such notification systems.
 With today’s technology, the picture has changed drastically and situations like on the picture should be a thing of the past. As many wireless water leak sensors you need communicating with your central hub/controller/gateway and in case of a flood the “smart home” will take action, which can be a simply notification via email or text, announcement within the house over all speakers, alarm sirens, etc the options of actions is very long.
With today’s technology, the picture has changed drastically and situations like on the picture should be a thing of the past. As many wireless water leak sensors you need communicating with your central hub/controller/gateway and in case of a flood the “smart home” will take action, which can be a simply notification via email or text, announcement within the house over all speakers, alarm sirens, etc the options of actions is very long.
This example doesn’t prevent any flooding, but it will take action at the slightest amount of water reaching the water leak sensors, which can prevent coming home to a completely flooded basement. Those costs will run in the thousands of dollars and the best of this whole example is: “Insurance companies will give you a discount, if you install water leak detection systems in your home”. Simply ask your insurance and they will tell you what discount you will receive, if you chose to implement this example.
This applies to home owners and landlords. The investment of having such a system implemented can be recovered after several months or years. Example would be a 10% discount for a home owner insurance of $1,500 per year. Those savings of $150/year would give you a break even point from your investment of 2 or 3 years, not to mention the cost savings of not having to repair a flooded basement or laundry room, which typically range in the area of $3,000 to $5,000 or more.
Energy Control
Another example would be energy control of your home. You could have remote controlled blinds, fans and thermostats in your home. You could use your cell phone, smart tablet or voice to turn those “connected devices” on as needed. A true “smart home” would do the following and this is just one example, which can be adjusted to any need or location…
IF summer AND IF morning AND IF temperature reaches 75 degrees –> THEN lower blinds
IF summer AND IF morning AND IF temperature reaches 75 degrees AND blinds lowered –> THEN turn on ceiling fan
IF summer AND IF morning AND IF temperature reaches 75 degrees AND blinds lowered AND ceiling fan is ON –> THEN power on air condition
 In simplified text, this logic does the following. In the morning, when the sun rises, the temperature in your house rises as well. Most households have their thermostat set to a certain temperature, before the air condition kicks in. Even if they have smart thermostats, they will get trigger by a certain temperature.
In simplified text, this logic does the following. In the morning, when the sun rises, the temperature in your house rises as well. Most households have their thermostat set to a certain temperature, before the air condition kicks in. Even if they have smart thermostats, they will get trigger by a certain temperature.
The example logic above delays the air conditioning kicking in by using the alternative methods of blocking out sun or using ceiling fans first before the more power hungry and costly air conditioning system kicks in. The “smart home” will try to block the sun first by lowering the blinds. If the temperature still rises, then the “smart home” will turn on the ceiling fan. Only if all that isn’t enough, then it will turn on the air condition.
Security and Fire Alarm
The top rated reason for people adopting “smart home technology” is security. The security industry has been around for many years and alarm systems have evolved in many directions over the years. Security systems today include not only window/door sensors, glass break and motion sensors, but also fire alarm detectors and cameras with motion alarm.
Having those notifications going to a service provider, who will call the authorities is a good thing. However, nobody has thought about the actual home owner in those situations. To be more specific, image a fire alarm going off in your home. The sirens will go off, you might get a call from your service provider and the whole family will be up in no time. What is not considered is, how to make this situation easier and less stressful.
 Imagine the same scenario, but in this case once the alarm goes off, the lights in the whole house will go on or change color to e.g. red, the blinds will open allowing a clear view from the outside into the house for the firemen, the alarm system will disarm after the authorities have been notified (last thing you need is your alarm system sirens going off just because you or your family opened the door and you forgot to enter the code to disarm the alarm system), the door locks will unlock allowing easy exit of the house, the speakers throughout the whole will announce that there is fire and with the right equipment it can also announce, where in the house fire has been detected. If nobody is home, the home owner will get notified via email, text or phone call from the service provider and from the smart home and having the doors unlocked will allow easy entry into the home for the firemen.
Imagine the same scenario, but in this case once the alarm goes off, the lights in the whole house will go on or change color to e.g. red, the blinds will open allowing a clear view from the outside into the house for the firemen, the alarm system will disarm after the authorities have been notified (last thing you need is your alarm system sirens going off just because you or your family opened the door and you forgot to enter the code to disarm the alarm system), the door locks will unlock allowing easy exit of the house, the speakers throughout the whole will announce that there is fire and with the right equipment it can also announce, where in the house fire has been detected. If nobody is home, the home owner will get notified via email, text or phone call from the service provider and from the smart home and having the doors unlocked will allow easy entry into the home for the firemen.
In summary, there is nothing wrong with having a “connected home”. As a matter of fact a connected home is the first step towards a smart home. Yes, it requires some adjustment and logic to be put in place, before a connected home becomes a smart home. The time is worthwhile investing, as the return of the investment will be worth it.
The additional cost of making a connected home to become a smart is much lower compared to making a regular home to become a connected home or smart home. The only challenge with this transformation from connected home to smart home will be the interoperability between the smart devices and the hub/controller/gateway, as not all vendors will support all smart devices.
 In some cases workarounds are available and yes, you could use something like IFTTT (If this then that) to create logic for your connected home. IFTTT has a wide variety of supported devices (channels), but you should consider always the worst case, which is when your home might not have any internet connection. Some home automation hub/controller/gateway vendors require an internet connection to be available to conduct any actions in your home, which might not be a good thing in some of the use cases and examples outlined above including IFTTT.
In some cases workarounds are available and yes, you could use something like IFTTT (If this then that) to create logic for your connected home. IFTTT has a wide variety of supported devices (channels), but you should consider always the worst case, which is when your home might not have any internet connection. Some home automation hub/controller/gateway vendors require an internet connection to be available to conduct any actions in your home, which might not be a good thing in some of the use cases and examples outlined above including IFTTT.
The smart home adoption is at an all-time high and I encourage everybody to invest the time to find the most suitable technology for their homes and families and aim for a true “smart home”.















